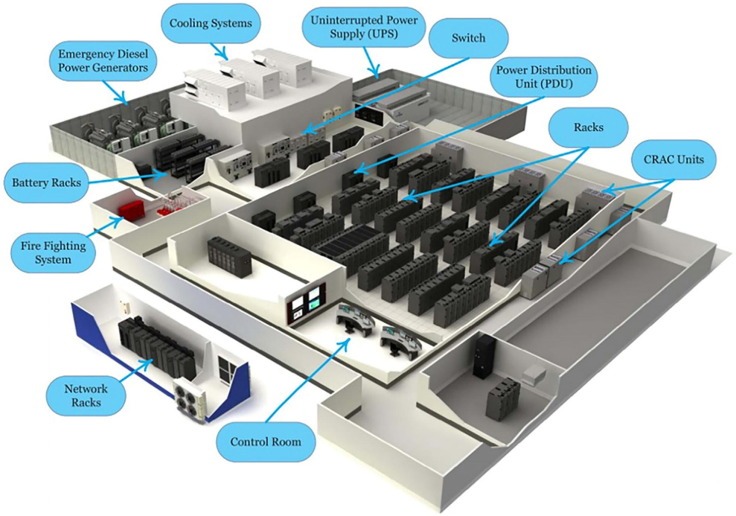
Data centres are constantly researching new battery technologies that deliver reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly ways to supply power in case of a power outage. Beeks Group dedicated servers Frankfurt data centres have been at the forefront of battery technologies for decades. The following are dependable, cost-effective, and ecologically friendly power alternatives for data centres.
-
Battery-Grid Integration
One of the main goals for data centre engineers at Microsoft and Google has always been to find battery technologies with a backup that have a lower footprint and incorporate with the local electrical grid. The primary constraint with innovative data centre batteries is how to manage it when it is powered off. The solution is to accumulate the excess power generated by the alternative power source by integrating it with the local energy grid.
The data centre will have energy reserves for backup power with the local energy supplier. The excess energy reserves with the local energy provider can also create a continuous revenue stream for the data centre.
-
Lithium-Ion Batteries
One of the most preeminent innovations in data centre battery technology is the swift advancement of the capabilities of lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries have become a replacement for obsolete lead-acid batteries because they have rapidly become more affordable. Lithium-ion batteries are lightweight but still deliver more power which converts into a smaller footprint from an infrastructural point of view for the data centre. Lead-acid batteries contain an electrolyte solution.
The implication is the data centre must maintain the temperature in the storage facility of the lead-acid batteries that increases heating and cooling costs. Lithium-ion batteries are more efficient because they do not contain electrolytes but still charge much faster than lead-acid batteries. The absence of electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries means that the data centre is not afflicted with the extra costs of cooling and heating the premises.
-
Nickel-Zinc Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular in recent times, but they aren’t the only battery technology variant in production. Thermal runaway is a serious concern with lithium-ion batteries. Thermal runaway is when the temperature of the battery is more than its ability to dissipate it safely. A chemical reaction occurs that discharges all of the energy in the battery which can cause a fire.
Nickel-zinc battery technology is an aqueous mixture so there is no risk of thermal runaway but the technology has not evolved as much as lithium-ion batteries. Government authorities require data centres to comply with safety codes to mitigate the risk of fire. Nickel-zinc battery alternatives provide just as much energy as a lithium-ion without the risk of thermal runaway.
Solutions To Alternative Power Sources
While it is not exactly a battery technology, many organizations consider shifting IT deployment to an integrated data centre to maintain high availability. The organization remains functional by coordinating IT operations and backing up systems with the colocation which acts as a data centre. The data centre can provide all of the IT functionality necessary to maintain uptime. The organization does not face excessive operational costs by coordinating with the data centre.